Part 1
The money market is defined as having three types of money. Commodity money is a currency standing for one thing. Representative money can be explained by things such as gold and silver, which represents a commodity. The third is Fiat money, which is the type that our country now runs by. This is money not backed by metal, and must be accepted through transactions.
The three functions of money are that it is a medium of exchange, a store of value, and a unit of account.
Part 2
The money market is represented as a money market graph, which we can show that if we increase demand, we raise interest rates. So, if we raise demand, we increase the pressure on interest rates. Supply is set by the fed, so when the demand increased, the quantity in money does not. If the money supply shifts to the right, the interest rates are stable.

Part 3
The Fed's tools of monetary policy are expressed in this segment video through contractionary and expansionary policy. Expansionary can be expressed as easy money, and in this, the RR is decreased as well as the discount rate. They also choose to buy bonds to increase there money supply. This is the opposite in contractionary policy, which is also known as tight money, because the RR increases as well as the discount rate. They choose to sell bonds to decrease this money supply.
RR can be defined as the percentage of a bank's total deposits that must be kept as vault cash or on reserve with the Federal branch. Lowered RR becomes excess reserves.
The discount rate is the rate at which banks borrow money from the Fed.
Part 4
The Loanable Funds Market can be defined as the money available in banks for people to borrow.

The Supply loanable funds comes from the amount of money that people have in banks. They are dependent on savings. So, the more money people save, the more money people will have to make loans.
In a deficit, the government demands money to spend.
2 ways to demonstrate a change in Loanable Funds
1) Increase in demand of loanable funds.
2) Decrease supply
Part 5
The money creation process is defined by how banks create money by making loans. If a banks holds excess reserves, it reduces total money supply. The potential total increase is defined by the Initial Loan x Money Multiplier.
Part 6

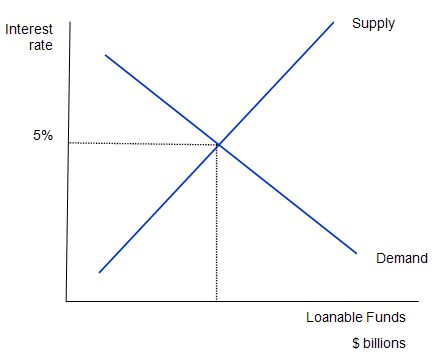

In the money market graph, we can see that the Money supply is controlled by the fed, therefore it is at a set amount. In loanable funds, the equilibrium rate and quantity stay the same. If there is deficit spending, the Money market has the government borrowing money from the people. There is an increase in demand as well as Interest rates. The Fisher Effect is represented, as it is the increase in interest rate, and it must have the same increase in price level.
No comments:
Post a Comment